Automating AWS pentesting at AutoScout24
Shivankar Madaan · December 14, 2022 · 3 min read
Introduction
Hello people, I am Shivankar and I have been at AutoScout24 for almost 2 years and it has been amazing security engineering journey. I have learned tons of ways to automate security operations. But for this part of the post, I will be focusing on one of our tasks of automating offensive AWS tasks.
AWS security
Due to the rapid increase in attack vectors across AWS services, it is becoming difficult to perform manual penetration operations across multiple accounts. As engineers, the first thing we wanted to do was to automate this so that we no longer have to spend time manually repeating the process for every account. So we created and released ThunderCloud, a tool to easily scale up the offensive operations at AutoScout24.
Scenarios
I’d like to briefly discuss a few scenarios.
Misconfigured Cognito Endpoints
Congito is a service from AWS to manage authentication and authorization. There is a very interesting feature in Cognito, named identity pool, which can allow authenticated or unauthenticated users to use/access AWS services using temporary credentials. Generally applications use this feature to provide end-users with the ability to upload their pictures to a static storage location, such as S3. However, mistakes can happen, and if not correctly, configured any attacker can get access to private S3 data.
IAM backdoor creation
As soon as someone gets valid AWS credentials, the first thing they would do is to enumerate for permissions. And if the role, associated with those credentials, has permissions to create IAM users, roles or policies, they can create backdoor users or roles which grant STS permissions to their own (attacker) AWS account. This allows to create persistence and, even if the SOC team deletes or rotates the exposed credentials, they still have a way to get back into the compromised account.
IAM enumeration and assumption
In few cases, if an IAM role has not been correctly configured, an attacker over the internet can enumerate the role based on some common names used across organizations such as devops, admin, developer, service, etc etc. In few rare cases this role is also assumable by any authenticated AWS user over the internet. All the red teamers need is the AWS account ID of the victim and wordlist of common roles names, making it very easy for red teamers to look out for such IAM roles.
Usage
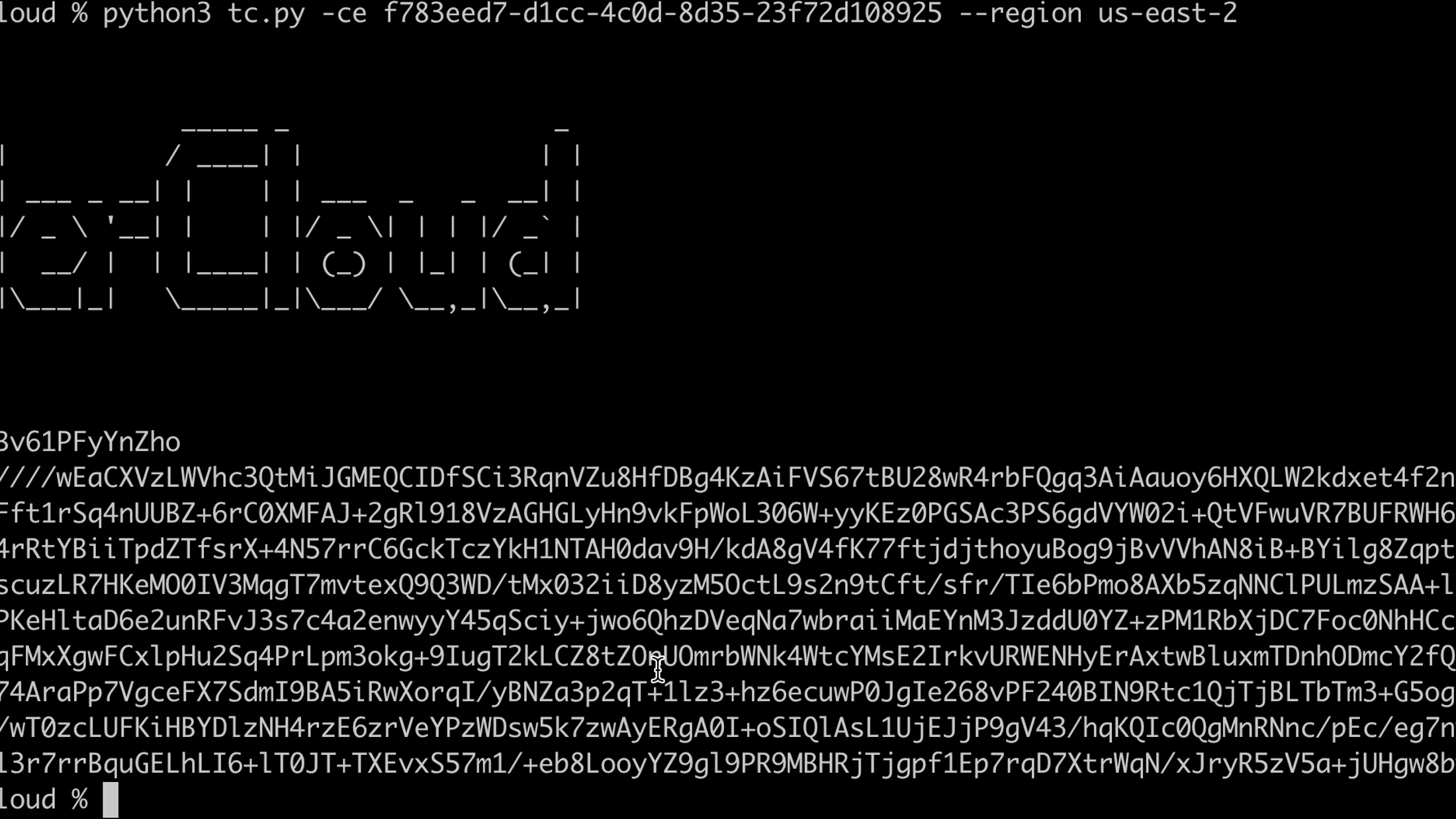
The tool is simple to use. Here’s how a snippet of the code execution looks like, when you run it for cases as described above.
Cognito endpoint
python3 tc.py -ce <cognito-endpoint> --region <aws-region>
IAM Backdoor role
python tc.py -bdrole <backdoor-role-name> -aws_key <access_key> -aws_secret <secret_key> -accid <aws_account_id>
Final statement
This tool has been presented at Blackhat Asia Arsenal and Blackhat Europe Arsenal. I’d like to thank my team Security Engineering for supporting and guiding me. We are working on really interesting projects all over the year and if you are interested to work with us you might want to check our careers page.






